Calgary, Canada
Make it Personal: How Calgary Is Supporting Residents to Take Climate Action.
Project Type:
Energy, Environment, Infrastructure and Utilities, Technology

At a Glance
The residential solar calculator helps Calgarians understand the potential for solar energy generation in their home. It provides an estimate of energy cost savings, greenhouse gas reductions and the investment payback period. This data supports Calgarians to make informed decisions on energy use in their home.
Applied advanced analytics to map data, 3D building models and energy costs to create a residential solar calculator tailored for Calgary households—an in-house solution that contributed to a doubling of the city’s residential solar installations in 2023.
48,000 visits to the online residential solar calculator, with 65% returning users, which shows high engagement from residents.
The importance of harnessing the power of the sun is clear. Worldwide, extreme weather events have increased fivefold since 1970 and 2024 was Canada’s costliest year on record for weather-related disasters. Calgary, Canada’s sunniest city, enjoying approximately 333 days of sun each year, and Canada’s fastest-growing metropolitan area with 1.68 million residents, recognizes that addressing climate change requires collective action. For individuals, it can be hard to know how to contribute. But The City of Calgary is empowering residents to act with a climate strategy that blends data, innovation and community engagement.
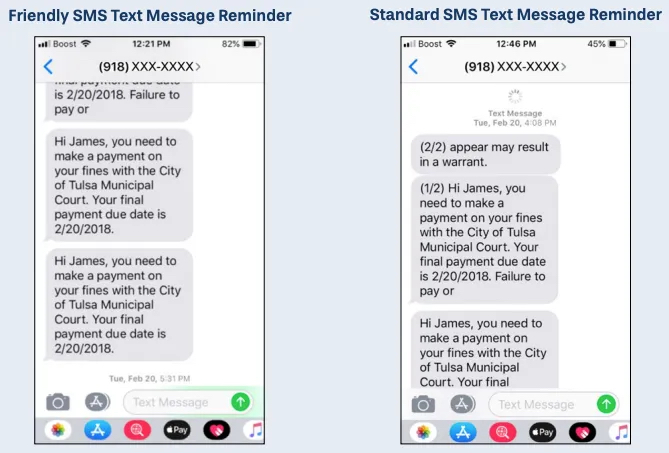
One standout initiative is Calgary’s Residential Solar Calculator. Launched in 2022, the online tool allows homeowners to assess their property’s solar potential. It uses LiDAR remote sensing and GIS mapping technology to account for roof tilt, orientation and shading and provides personalized solar insights for each Calgary residential address. The tool equips residents with vital knowledge to weigh the pros and cons of solar energy and engage with service providers confidently. The calculator educates homeowners on switching to solar energy, providing an estimated upfront cost and monthly energy savings. This information is crucial for determining whether solar energy is financially viable and how quickly the investment will pay off.

“Data analysis, visualization and data-supported stories play an incredibly important role in our climate work today and the climate work of tomorrow. We are using data to help us understand the complex nature of climate systems, identify patterns and trends, inform action and communicate with Calgarians.”
To support Calgary’s broader greenhouse gas reduction goals, The City wants to generate more of its electricity needs within city boundaries from renewable sources. In 2023 alone, Calgary installed 16,000 kilowatts of residential solar PV—doubling the city’s capacity. During this time, more than 48,000 people have visited the calculator and almost two-thirds are return users, signaling high engagement. The popularity of the calculator highlights that there is an appetite from Calgarians to explore and understand the benefits of installing solar energy in their homes. By providing easily accessible, relevant and tailored information to homeowners, the residential solar calculator helps drive solar adoption indirectly through education and information sharing.
Supporting these efforts is Calgary’s comprehensive climate and environment dashboard, which tracks metrics and shares key program information with residents. This dashboard will ensure The City is transparent and accountable to its climate goals and outcomes by providing a comprehensive resource for the community to monitor results.
“Calgary is committed to embedding data and evidence into our decision-making processes. This approach ensures that taxpayer dollars are used effectively and that Calgary is a stronger and more resilient city, capable of facing future challenges.”
Climate change is a global challenge, but Calgary’s approach shows the power of solutions that involve government and residents. By making climate information more personalized and accessible to all, Calgary is not only addressing the crisis—it’s demonstrating its commitment to support its residents and setting a benchmark for other cities.