Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA
Tulsa Scales Up Data-First Innovation.
Project Type:
Communications, Cross-Sector, Economic Development
Tulsa most recently achieved 2024 Silver What Works Cities Certification. The following narrative was written for Tulsa’s 2020 Silver What Works Cities Certification. Some content may be outdated. For the most current information, please visit cityoftulsa.org.
At a Glance
Created a cross-departmental team that identifies the most effective methods for achieving the city’s top goals and leads the city’s data-driven transformation.
Found patterns in 911 repeat call data that signaled the need for a new referral program to deliver specialized healthcare and social services for residents. Within the first three months of launching the program, there was a 70% reduction in calls from its top 911 utilizers.
Partnered city agencies and civic tech nonprofits to develop a text reminder system that reduced missed fines and warrants that have helped the City’s Court see an annual 187,000 increase in revenue.
Using Data to Power Innovation
G.T. Bynum has leadership in his veins. One of the youngest people ever elected mayor of Tulsa, Oklahoma, he’s the fourth person in his extended family to serve in the role since the turn of the last century. But he is the city’s first mayor to place data-driven decision making at the top of a change agenda. Since becoming mayor in December 2016, his administration has marked a turning point in how Tulsa uses data to power innovation and improve the quality of life in Tulsa.
Mayor Bynum didn’t waste any time after being elected. The idea of improving city services and using data to make key decisions was at the core of his mayoral campaign. One of his first moves as Mayor was the creation of the Office of Performance Strategy and Innovation (OPSI). The office works to align the city’s top goals with effective strategies. It quickly became key to the city’s data-driven transformation, says James Wagner, who led OPSI at its inception and is now the city’s director of finance and CFO.
Ben Harris, OPSI’s Data Analytics Manager, convened a team of employees from 16 departments to lead the city’s data governance and strategic planning efforts. The Data Governance Committee, which sets the standard and strategy for data quality, integrity, and use for the city government, has helped integrate the use of data citywide through the creation of a Central Data Repository where any employee or resident can request data.
“Through this cross-departmental team, we encourage transparency, access to data, and a feedback loop; ultimately it creates a trust relationship between departments,” Harris said.
“In addition to teamwork, technology played a huge role in orchestrating communication, automating data movement, securing data, and making it accessible.”
OPSI and the Committee also facilitate regular sessions with department leaders to focus on the value of performance metrics. These meetings aren’t just about tracking progress reviewing data — they’ve created a new space within the city to cultivate innovation.
“Mayor Bynum and other city leaders have consistently looked to OPSI to drive data-driven innovation work in Tulsa. This matters because we’re making real changes that improve city services and save taxpayers money.”
A Caring Fire Department
For years, the number of calls to the Tulsa Fire Department was increasing, putting stress on their resources and capacity. By analyzing the data, the fire department discovered the source of the increased calls was not an increase in fires, but instead an increasing aging population who needed lift assists. Lift assists are calls to the 911 system for a non-emergency fall — the help the resident is requesting is to literally be picked up off of the ground. The city discovered a repeat lift assist pattern, with some residents requesting a lift assist as many as nine times a day.
Under the direction of Chief Michael Baker, the Fire Department developed and launched the Tulsa Community Assistance Referral and Educational Services (CARES) program, which was designed to connect high-utilizers of the emergency system to healthcare and social service providers. Visits to the highest utilizers became proactive, with the CARES team working on simple fixes such as installing low-cost solutions like handrails and opening up a dialogue with the resident’s primary care doctor. Within the first three months of the pilot, the fire department saw a 70 percent reduction in calls from its top 911 utilizers.
With preliminary results in hand, Baker presented his findings through the TulStat forum.
“TulStat,” based on the successful “LouieStat” program out of Louisville, Kentucky, has created a forum for change in Tulsa. City leaders gather to discuss priority problems, define success, innovate solutions, and develop methods for measuring progress. They identify specific, quantifiable goals, such as average time for reviewing building permit applications (previously 5 weeks, now 92 percent completed in 5 days) or responding to a 911 call, and troubleshoot obstacles to achieving them.
While CARES was developed before Bynum’s administration founded TulStat, having a space to build off of the pilot’s success was critical in connecting more residents to much-needed services. The program has served 204 clients; in 2020, four Tulsans have “graduated” the program and have the needed support services in place for them to live safely in their homes.
In the future, CARES hopes to work with OPSI to expand their data capacity to learn how to predict who is at risk for becoming a repeat caller to the 911 system and intervening early to distribute tools and services. Aligning community resources to provide innovative, proactive care will not only save the city’s Medicare and Medicaid partners money, it could save a resident’s life.
Breaking the Cycle
Working with What Works Cities and the Behavioural Insights Team, OPSI also helped the Tulsa Municipal Court solve a problem that had burdened the court and vulnerable residents for years.
Previously, when the court issued a resident a fine in a criminal case, but that resident wasn’t able to pay that fine on time, the court would offer an extension in the form of a “Time to Pay Order.” Some found themselves with a fine due more than 12 months in the future — enough time for them to save money for the payment, but also plenty of time to forget when it was due. As of early 2018, more than 70 percent of those orders resulted in a failure-to-pay warrant. For many, a warrant can exacerbate the cycle of poverty: a driver’s license might be suspended and additional fines can accrue, pulling someone further into the criminal justice system.
To combat the problem, OPSI partnered with the Court and Code for Tulsa to figure out how to reduce the number of warrants issued. Within a month, a text message pilot project was underway, designed around a simple hypothesis: Many people missed their Time to Pay Order deadline because they forgot the due date or lost paperwork. Together, OPSI, the Court, and Code for Tulsa developed a system to text simple, personalized reminders to a randomly selected pool of Time to Pay Order recipients. The test group received a text message reminder once a month leading up to their deadline.
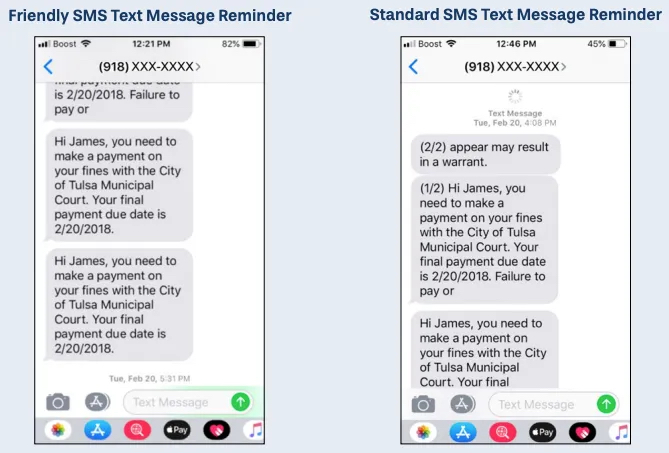
The results were remarkable. During the six-month pilot, 63 percent of those who received a reminder paid all of their outstanding fees, compared to 48 percent of residents who did not receive reminders. Armed with data showing this 15 percent point increase, the Court system adopted the new reminder system. It now estimates an additional 320 people are paying their fees on time each year, avoiding warrants and additional problems because of the system. The Court benefited as well, seeing an annual $187,000 increase in revenue and a morale boost among employees who helped implement the solution.
“I’ve never been so excited about a job,” said Jamie King, a cost administrator at the court.
At the City’s Core
OPSI’s successful partnerships with city departments go beyond the fire department and courts. Three years in, OPSI has implemented practices and programs that have positioned Tulsa as a leader in data and innovation. In 2017, the office launched Urban Data Pioneers, an award-winning program consisting of teams of residents and city employees who analyze data to help the city solve key challenges and present policy recommendations.
With OPSI’s clear-cut ability to drive innovation, Mayor Bynum decided to integrate the office into the city’s key funding decisions. When Wagner became Director of Finance and CFO in early 2019, he brought OPSI with him to the Finance Department. This has changed the way Tulsa funds innovation. In essence, a data-driven approach has been institutionalized and scaled. Today, the city bases funding on data that proves programs work. OPSI vets data.
“We had the opportunity to take the approach and plug it into the finance department,” Mayor Bynum said. “It helps make it have much more of a citywide cultural impact.”